Here this topic will explain RACH procedure 5G/NR basically about the 4-Step Rach procedure. Also as you know 2 step RACH is also introduced in NR/5G release 16. So let’s start with basic questions as below.
What is 4 Step RACH Procedure?
RACH is the first uplink message which is sent by the UE to the Network for uplink synchronization via the PRACH channel and RACH is handled by the MAC Layer.
In LTE and NR there is a basic difference in the RACH procedure LTE there was no concept of the beam but, In NR SSB (Synchronization Signal / Physical Broadcast Channel (SS/PBCH) Blocks) is associated with the different beams.
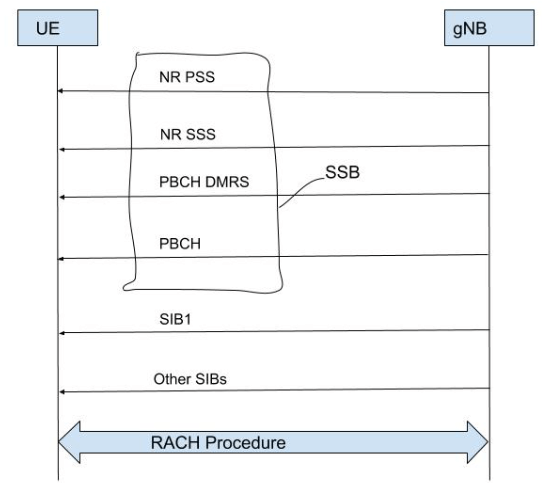
UE selects the best beam which has good reference signal power and sends PRACH using that beam.
Types of RACH:
There are two types of RACH for 5G(SA) and NSA as 3GPP specification terms we called CBRA and CFRA.
- Content-Based Random-Access Procedure (CBRA)
- Contention Free Random-Access Procedure (CFRA)
Also Read :- what-is-redcap-reduced-capability-in-nr-3gpp-r17-release
Content-Based Random-Access Procedure (CBRA):
The content-Based Random-Access Procedure happened when UE doesn’t have assigned dedicated parch preambles to perform the RACH procedure, in the case of the Contention-based Rach procedure UE randomly selects the preambles out of 64 preambles.
so there is a probability multiple UE sends the same preambles to the network at the same TTI (Transmission Time Interval) then a collision with happened this type of procedure is a Contention Based procedure.
For example, Three UE sends the same preambles to the network (GnodeB) then the network out of three UE only sends the Contention Resolution to the one UE for that UE RACH successful, and the other UE must perform the 4-Step RACH procedure again.
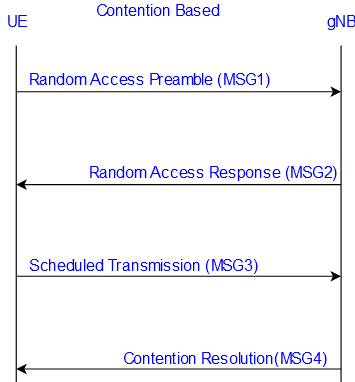
CBRA procedure performed below scenario:
- Initial Access Procedure or RRC Connection Setup Procedure
- RRC-Reestablishment Procedure
- Uplink Data Arrival
- Uplink data arrival during RRC_CONNECTED when no PUCCH resources for SR are available.
- If UE needs to schedule something (Scheduling Request (SR) procedure).
Contention-Free Random-Access Procedure (CFRA):
The contention Free Random-Access procedure has dedicated preambles assigned to UE by Network (GnodeB) hence there is no chance of collision so that’s why it’s called a Contention Free Random Access procedure. Dedicated preambles are assigned to UE via RRC signaling and it’s a three-step procedure.
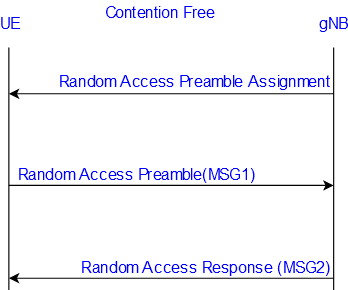
CFRA procedure performed below scenario:
- During Handover Contention free Rach performed
- During NSA (NR Cell Addition) via RRC Connection reconfiguration CFRA performed
- Downlink Data Arrival (DL-SCH) PDCCH Order
- During the transition of RRC INACTIVE to RRC CONNECTED mode
- During On-Demand SI(System Information Block)
- During Beam Recovery
In LTE generally, we get the RACH IE’s or information element under SIB2 for Contention based and Contention free we get the IE’s under RRC Connection Reconfiguration but In NR, CBRA Contention Based Random Access IE’s comes under SIB1 only for CFRA same as LTE comes under RRC Connection Reconfiguration.
CFRA (Contention Free RACH Procedure) RACH Configuration Information Elements(SIB 1):
Below are RACH Config IEs based on the 3GPP 38.331 version 17.2.0
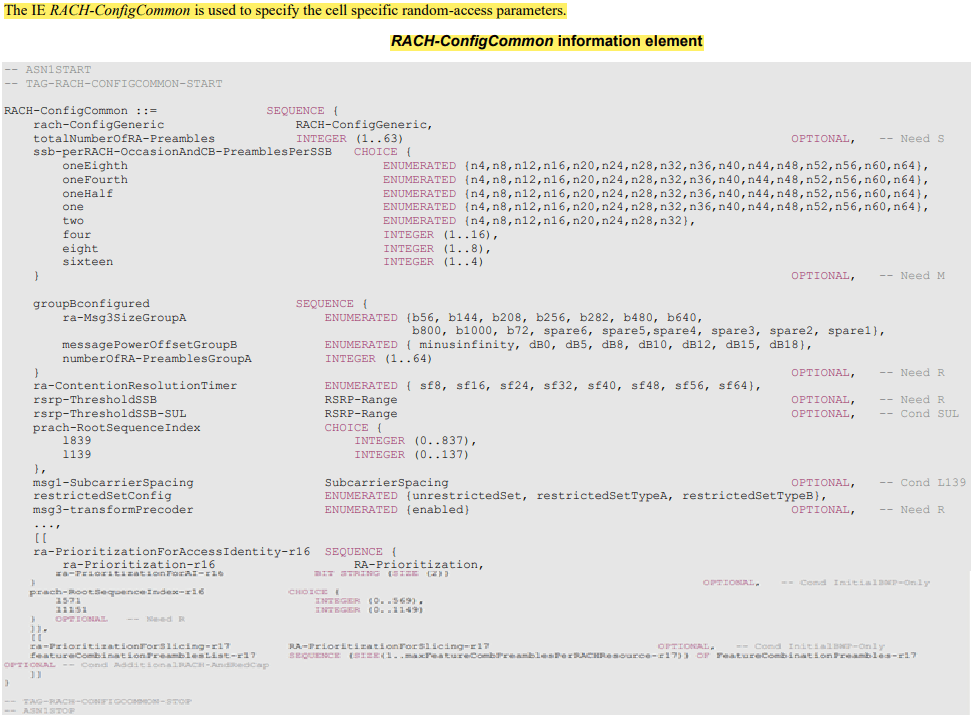
featureCombinationPreamblesList Specifies a series of preamble partitions each associated to a combination of features and 4-step RA. The network does not configure this list to have more than 16 entries.
messagePowerOffsetGroupB Threshold for preamble selection.
- Value is in dB.
- Value minus-infinity corresponds to –infinity.
- Value dB0 corresponds to 0 dB, dB5 corresponds to 5 dB, and so on. (see TS 38.321 [3], clause 5.1.2)
msg1-SubcarrierSpacing Subcarrier
spacing of PRACH (see TS 38.211 [16], clause 5.3.2). Only the following values are applicable depending on the used frequency:
FR1: 15 or 30 kHz FR2-1: 60 or 120 kHz, FR2-2: 120, 480, or 960 kHz
If absent, the UE applies the SCS derived from the prach-ConfigurationIndex in RACH-ConfigGeneric (see tables 6.3.3.1-1, Table 6.3.3.1-2, Table 6.3.3.2-2 and Table 6.3.3.2-3, TS 38.211 [16]).
The value also applies to contention-free random access (RACH-ConfigDedicated), SI-request, and contention-based beam failure recovery (CB-BFR). But it does not apply for contention-free beam failure recovery (CF-BFR) (see BeamFailureRecoveryConfig)
msg3-transformPrecoder Enables the transform precoder for Msg3 transmission according to clause 6.1.3 of TS 38.214 [19]. If the field is absent, the UE disables the transformer precoder (see TS 38.213 [13], clause 8.3)
numberOfRA-PreamblesGroupA The number of CB preambles per SSB in group A. This determines implicitly the number of CB preambles per SSB available in group B. (see TS 38.321 [3], clause 5.1.1). The setting should be consistent with the setting of ssb-perRACH-OccasionAndCB-PreamblesPerSSB.
prach-RootSequenceIndex
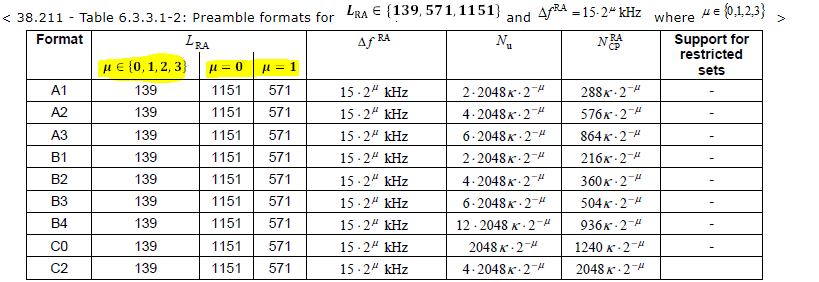
PRACH root sequence index (see TS 38.211 [16], clause 6.3.3.1). The value range depends on whether L=839 or L=139 or L=571 or L=1151.
The length of the root sequence corresponding with the index indicated in this IE should be consistent with the one indicated in prach-ConfigurationIndex in the RACH-ConfigDedicated (if configured).
If prachRootSequenceIndex-r16 is signalled, UE shall ignore the prach-RootSequenceIndex (without suffix).
For FR2-2, only the following values are applicable depending on the used subcarrier spacing:
120 kHz: L=139, L=571, and L=1151
480 kHz: L=139, and L=571
960 kHz: L=139
ra-ContentionResolutionTimer The initial value for the contention resolution timer (see TS 38.321 [3], clause 5.1.5). Value sf8 corresponds to 8 subframes, value sf16 corresponds to 16 subframes, and so on.
ra-Msg3SizeGroupA Transport Blocks size threshold in bits below which the UE shall use a contention-based RA preamble of group A. (see TS 38.321 [3], clause 5.1.2).
ra-Prioritization Parameters which apply for prioritized random access procedure on any UL BWP of SpCell for specific Access Identities (see TS 38.321 [3], clause 5.1.1a)
ra-PrioritizationForAI Indicates whether the field ra-Prioritization-r16 applies for Access Identities. The first/leftmost bit corresponds to Access Identity 1, the next bit corresponds to Access Identity 2. Value 1 indicates that the field ra-Prioritization-r16 applies otherwise the field does not apply (see TS 23.501 [32]).
ra-PrioritizationForSlicing Parameters which apply to configure prioritized CBRA 4-step random access type for slicing.
rach-ConfigGeneric RACH parameters for both regular random access and beam failure recovery.
restrictedSetConfig Configuration of an unrestricted set or one of two types of restricted sets, see TS 38.211 [16], clause 6.3.3.1.
rsrp-ThresholdSSB UE may select the SS block and corresponding PRACH resource for path-loss estimation and (re)transmission based on SS blocks that satisfy the threshold (see TS 38.213 [13]).
rsrp-ThresholdSSB–SUL The UE selects SUL carrier to perform random access based on this threshold (see TS 38.321 [3], clause 5.1.1). The value applies to all the BWPs and all RACH configurations.
ssb-perRACH-OccasionAndCB-PreamblesPerSSB
The meaning of this field is twofold: the CHOICE conveys the information about the number of SSBs per RACH occasion. Value oneEighth corresponds to one SSB associated with 8 RACH occasions, value oneFourth corresponds to one SSB associated with 4 RACH occasions, and so on.
The ENUMERATED part indicates the number of Contention Based preambles per SSB. Value n4 corresponds to 4 Contention Based preambles per SSB, value n8 corresponds to 8 Contention Based preambles per SSB, and so on.
The total number of CB preambles in a RACH occasion is given by CB-preambles-per-SSB * max(1, SSB-per-rach-occasion). See TS 38.213 [13].
totalNumberOfRA-Preambles Total number of preambles used for contention based and contention free 4-step or 2-step random access in the RACH resources defined in RACH-ConfigCommon, excluding preambles used for other purposes (e.g. for SI request).
If the field is absent, all 64 preambles are available for RA. The setting should be consistent with the setting of ssbperRACH-OccasionAndCB-PreamblesPerSSB, i.e. it should be a multiple of the number of SSBs per RACH occasion.
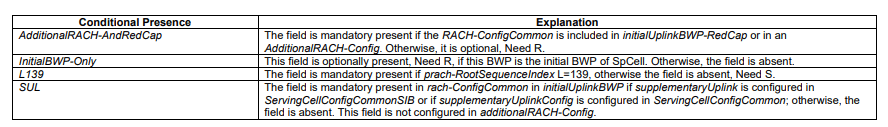
CBRA (Contention Based RACH Procedure) RACH Configuration Information Elements (SIB 1):
Below RACH Config IEs based on the 3GPP 38.331 version 17.2.0.
csi-RS The ID of a CSI-RS resource defined in the measurement object associated with this serving cell.
ra-OccasionList
RA occasions that the UE shall use when performing CF-RA upon selecting the candidate beam identified by this CSI-RS. The network ensures that the RA occasion indexes provided herein are also configured by prach-ConfigurationIndex and msg1-FDM.
Each RACH occasion is sequentially numbered, first, in increasing order of frequency resource indexes for frequency multiplexed PRACH occasions; second, in increasing order of time resource indexes for time-multiplexed PRACH occasions within a PRACH slot and third, in increasing order of indexes for PRACH slots.
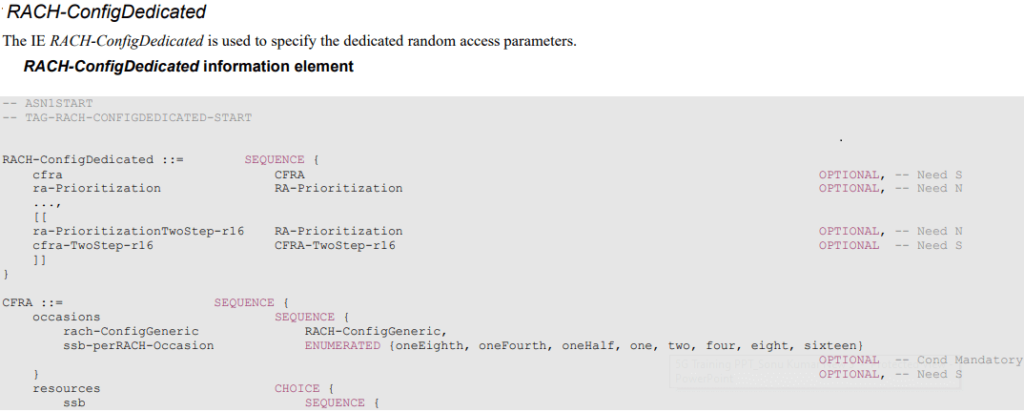
ra-PreambleIndex the RA preamble index to use in the RA occasions associated with this CSI-RS.
occasions RA occasions for contention-free random access. If the field is absent, the UE uses the RA occasions configured in RACH-ConfigCommon in the first active UL BWP.
ra-ssb-OccasionMaskIndex
Explicitly signalled PRACH Mask Index for RA Resource selection in TS 38.321 [3]. The mask is valid for all SSB resources signalled in ssb-ResourceList.
rach-ConfigGeneric Configuration of contention-free random-access occasions for CFRA. The UE shall ignore preambleReceivedTargetPower, preambleTransMax, powerRampingStep, raResponseWindow signaled within this field and use the corresponding values provided in RACH-ConfigCommon.

ssb-perRACH-Occasion Number of SSBs per RACH occasion.
totalNumberOfRA-Preambles
A total number of preambles used for contention-free random access in the RACH resources defined in CFRA, excluding preambles used for other purposes (e.g. for SI request).
If the field is absent but the field occasions is present, the UE may assume all the 64 preambles are for RA. The setting should be consistent with the setting of ssbperRACH-Occasion, if present, i.e. it should be a multiple of the number of SSBs per RACH occasion.
Sequence Length in NR RACH Procedure:
In LTE, there is only one type of sequence length, i.e. Short Sequence, but in NR, we have two types: Short Sequence and Long Sequence.
Note:- FR1:- Short and Long both sequence lengths can be used.
FR2:- short sequence length only used.
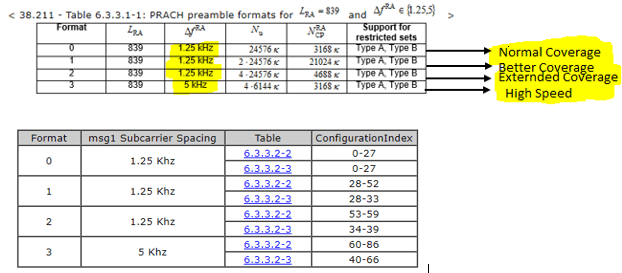
Long Sequence:
In NR, the long sequence is used for only FR1 cells. In the long sequence, we have four formats same as LTE. And subcarrier spacing of the long sequence is 1.25KHZ and 5KHZ.
Short Sequence:
In NR, the short sequence we used for both FR1 and FR2. In the short sequence, we can define the subcarrier spacing according to the u (0,1,2,3) value. Here we can only have 139 sequences.
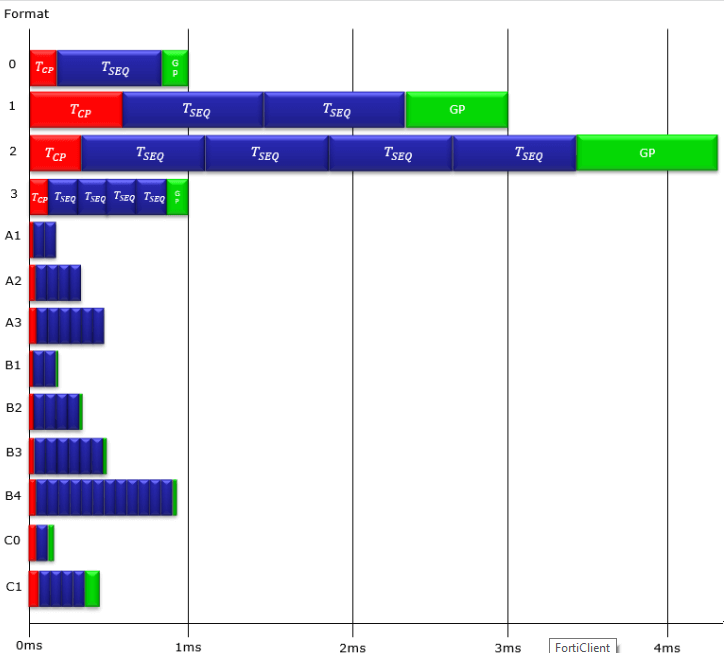
This picture of time domain resource allocation of both short and long sequences of all RACH preamble. Just pay attention to relative length differences among different types.
The parch config index is the main discussion point here so PRACH config index we have two types of tables paired spectrum table for the FDD band FR1 and an unpaired spectrum table for the TDD band FR1 and FR2 in 3GPP specification 38.211.