In this article, we will discuss the 5G Architecture & 5G network elements in depth, the difference between the different networks and LTE, and the similarities.
Before going to study any technology first we must clear about what is the base model of that technology and how is different from other technology and what other components added on that why they required so I am going to discuss that in detail.
What is the difference between LTE and NR architecture?
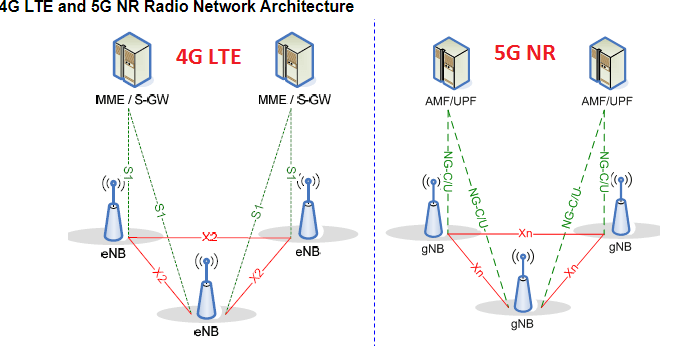
One of the main differences between 4G and 5G architecture is 5G we have two types of architecture and in 4G we have only one architecture.
-4G we don’t have any services like cloud-based or Virtual radio access networks (called RAN) but 5G(NR) technologies are designed to take advantage of cloud-based or virtual Radio Access Networks (called RANs). The providers can even take advantage of localized Data Centers to provide a consistently faster and more reliable internet connection to users.
-In 4G we have MME which is handling all mobility-related functionality but in 5G we have AMF it’s the same as MME functionality after part mobility it’s also handling the Responsible for Connection and Reachability management, and location services.
-In 4G we have HSS for authentication and storing the user data but in 5G(NR) architecture, we have two separate elements for the same UDM for storing the user profile and AUSF for authentication service.
-4G we don’t have any beamforming or beam management functionality but 5G is totally based on beamforming services.
Also Read:- 4 Step RACH Procedure 5G/NR with IE’s
5G architecture Types
5G(SA) we have two types of architecture 5G Core architecture and 5G Service Based Architecture. Why is that such a requirement in 5G?
Basically, 5G core architecture is like other technology architecture (4G, 3G and 2G) it’s had own sets of network elements, but 5G Service based architecture can use the service from vendors and take the service and give the service according to requirements it’s like a cloud computing it uses the virtualization techniques.
5G Reference Point Architecture:
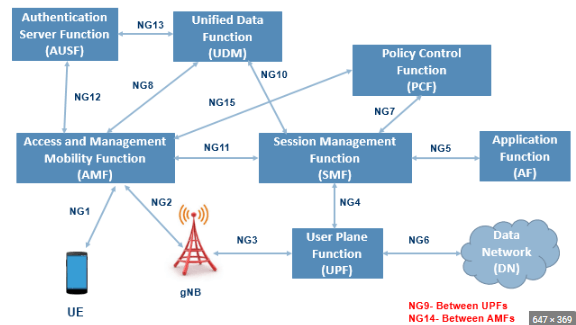
NR Service-Based Architecture:

5G Architecture Network Elements:
UE (User Equipment): Next generation 5G UE (User Equipment)
GnodeB: Next generation Node Base Station
AMF (Access and Mobility Management Function):
As its name defined Access and mobility management function.
AMF is the single point of contact to the UE like LTE MME is the single point of contact to the UE. It’s helping the UE to get grants, authentication, and communication with other layers.
Responsible for Connection and Reachability management, Mobility management, Access authentication, and authorization.
As you can see in the picture AMF connects to all nodes like UDM, AUSF, PCF, SMF, and GnodeB.
It’s responsible for the location services and managing the mobility-related aspects of the EPC’s MME.
SMF (Session Management Function):
Session Management so its main function is to manage the session between the UE and GnodeB.
-Session Management
-Data Notification Management (Downlink)
-Signaling Procedure
-IP Address allocation and management (UE)
-Termination of Session Management only for the NAS messages
– Management of Policy and Charging
UPF (User Plane Function): UPF is like a P-GW in LTE. UPF is the single point of contact to connect to the DN (Data network). And assign the IP to the UE. The main function is:
-PDU session management and managing the multi-PDU session simultaneously.
-QOS Flow handling
-Packet routing and forwarding
-Anchor point for Intra/Inter-RAT mobility
DN (Data Network): It’s provided internet service, IP address, and operator services.
UDM (Unified Data Management):
It acts like an HSS on LTE. Same functionality as UPF in 5G(SA). It stores the user subscription information and stores user data for authentication for AKA.
-Manage the authorization and subscription handling
-User Identification handling
-Generation of AKA credentials
AUSF (Authentication Server Function):
Its functionality is to perform an authentication process with the UE-like AAA server in LTE.PCF (Policy Control Function): Same works as the LTE PCRF node it’s managed the policy rules to control the plane. Manage the policy and subscription information.
Also Read:- What is REDCAP (Reduced Capability) in NR 3GPP R17 Release? What is NCD-SSB and CD-SSB in REDCAP NR R17?




